CTET January 2012 Question Paper-2 with Answer | ||||
| Child Development | Math and Science | Social Science | Language-I (Eng) | Language-II (Hindi) |
Candidate have to do questions number 31 to 90 either from Part-II ( Mathematics and Science ) or from Part-III ( Social Studies/ Social Science):
Part-II: Math and Science
Directions( Q. 31 – 90): Answer the following questions by selecting the most appropriate option.
Q31. 4 – (2 – 9)0 + 32 ÷ 1 +3 is equal to
(a) 17
(b) 16
(c) 15
(d) 12
| Answer: (c) 15 Solution: 4 – (2 – 9)0 + 32 ÷ 1 +3 = 4 – 1 + 9 + 3 = 15 |
Q32. Which of the following fractions is the least?
(a) 24/25
(b) 10/11
(c) 99/100
(d) 68/69
| Answer: (b) 10/11 Explain: If the difference between the numerator and denominator of every fraction is same then the fraction with the least value numerator will be least fraction and the greatest value numerator will be greatest fraction. Here difference between the numerator and denominator of every fraction is 1 And the fraction with the least value numerator is 10/11 So least fraction is 10/11 |
Q33. When the number 398 is divided by 5, the remainder is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
| Answer: (d) 4 Explain: Let the remainder is R Rof3985=Rof[(34)24×325]=Rof[{Rof(34)245×Rof325}5]NowRof(34)245=Rof81245=Rof(80+1)245=1 (usingRof(ax+1)na=1)andRof325=4∴Rof3985=Rof1×45=4 |
Q34. Two positive numbers x and y are inversely proportion. If x increase by 10
(a) 10
(b) 2/11
(c) 100/11
(d) 10/11
| Answer: (c) 100/11 Solution: y decreases by = 10110×100 =10011 Trick: If two positive numbers a and b are inversely proportion and a increase by x |
Q35. How many times I will be writing 2 if I wrote down numbers from 11 to 199?
(a) 36
(b) 37
(c) 38
(d) 39
| Answer: (d) 39 Explain: Any digit from 2 to 9 is used 20 times to write from 1 to 100. Only 1 is used 21 times. ∴ 2 is used to write from 11 to 100 = 20 – 1 = 19 Any digit from 1 to 9 is used 20 times to write from 101 to 200. Only 2 is used 21 times. ∴ 2 is used to write from 101 to 199 = 21 – 1 = 20 ∴2 is used to write from 11 to 199 = 19 + 20 = 39 |
Q36. The expression x2 – y2 + x + y – z2 +2yz – z has one factor, which is
(a) y – x + z
(b) x – y + z + 1
(c) x + y – z + 1
(d) x – y – z + 1
| Answer: (b) x – y + z + 1 Solution: x2 – y2 + x + y – z2 +2yz – z = x2 – (y2 – 2yz + z2) +x + y – z = (x – y + z) ( x + y – z) + ( x + y – z) = ( x + y – z) ( x – y + z +1 ) ∴ ( x – y + z +1 ) is a factor of given expression. |
Q37. Given n numbers, n>1, of which one is 1- 1/n and all others 1’s. The mean of the n numbers is
(a) 1
(b) n – 1/n2
(c) n – 1/n
(d) 1 – 1/n2
| Answer: (d) 1 – 1/n2 Solution: value of one number is 1 – 1n and (n – 1) numbers =1 Sum = (n−1)×1+1 −1n=n−1n Means = ( sum/ total numbers) = n−1nn=1−1n2 |
Q38. Shown here are expressions given to Seema, Anees, Asha, and Tessy with their answers.
Seema: 4 × 1 + 8 ÷ 2 = 8
Anees: 6 + 4 ÷ 2 – 1 = 4
Asha: 9 + 3 × 2 – 4 ÷ 2 = 10
Tessy: 27 ÷ 3 – 2 × 3 = 21
Who has get the correct answer?
(a) Seema
(b) Anees
(c) Asha
(d) Tessy
| Answer: (a) Seema Solution: 4 × 1 + 8 ÷ 2 = 4 + 4 = 8 |
Q39. If A = 3/4 ÷ 5/6
B = 3 ÷ [(4 ÷ 5) ÷ 6]
C = [3 ÷ (4 ÷ 5)] ÷ 6
D = 3 ÷ 4(5 ÷ 6)
(a) A and B are equal
(b) A and BC are equal
(c) A and D are equal
(d) All are equal
| Answer: (c) A and D are equal Solution: A = 34÷56=3×64×5=0.9 B = 3 ÷ [(4 ÷ 5) ÷ 6] = 3(45÷6)=345×6=3×5×64=22.5 C = [3 ÷ (4 ÷ 5)] ÷ 6 = (3÷45)6=3×546=3×54×6=0.625 D = 3 ÷ 4(5 ÷ 6) = 34(56)=3×64×5=0.9 |
Q40. Given numbers 3.75 × 10–7, 3¾ × 10–7, 375 × 10–9 and 3/8 × 10–7, which of these is not equal to 0.000000375
(a) 3.75 × 10–7
(b) 3¾ × 10–7
(c) 375 × 10–9
(d) 3/8 × 10–7
| Answer: (d) 3/8 × 10–7 Solution: 3.75 × 10–7 = 0.000000375, 3¾ × 10–7= 3.75 × 10–7 = 0.000000375, 375 × 10–9 = 0.000000375, all are same but 3/8 × 10–7 = 0.0000000375 |
Q41. The diameter of a cylindrical jar is increased by 25
(a) 10
(b) 25
(c) 36
(d) 54
| Answer: (c) 36 Solution: If diameter of a cylindrical increased then radius also same increased. Let initial radius (r1)= 100r and height (h1) = 100h Volume(v1) = π (100r)2.100h = 1000000πr2h Now Volume (V2) = π (125r)2.h2 = 1000000πr2h ⇒ h2 = 1000000h/15625 = 64h = 100h – 36h Height decreased 36 |
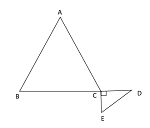
Q42. In the figure, ABS is an isosceles triangle with CA = CB and BC is produced to a point D. If CE BC such that ∠D = 1/2∠E = 1/2∠A, then measure of ∠ACD is
(a) 110°
(b) 120°
(c) 135°
(d) 140°
| Answer: (b) 120° Solution: ∠D + ∠E = 90° ⇒ ∠D + 2∠D = 90° ⇒∠D = 30° ∴∠E = 60° ∴ ∠A = 60° and ∠B = 60° ( CA = CB ) ∴∠ACD = 60° + 60° = 120° |
Q43. A large basket of fruits contains 3 oranges, 2 apples and 5 bananas. If a fruit is chosen at random, what is the probability of getting an orange or a banana?
(a) 4/5
(b) 1/2
(c) 7/8
(d) 1/5
| Answer: (a) 4/5 Explain: probability of getting an orange P(A) = 3/10 probability of getting a banana P(B) = 5/10 probability of getting an orange or a banana P( A or B) = P(A) + P(B) = 3/10 + 5/10= 4/5 |
Q44. The symbol ![]() , drawn to any size means a + 4, and the symbol
, drawn to any size means a + 4, and the symbol ![]() , drawn to any size means b2, where a and b are numbers. Then the value of
, drawn to any size means b2, where a and b are numbers. Then the value of ![]()
(a) 75
(b) 35
(c) 32
(d) 9
| Answer: (b) 35 Explain: = (3 + 4)2 + (2 + 4) – 42 + 4 = 49 + 6 – 20 = 35 |
Q45. If xy = 6 and x2y + xy2 + x + y = 63, then the value of x2 + y2 is
(a) 23
(b) 55
(c) 61
(d) 69
| Answer: (d) 69 Explain: 6x + 6y + x + y = 63 (put xy = 6) ⇒ 7(x + y) = 63 ⇒ x + y =9 Now x2 + y2 = (x + y)2 – 2xy = 81 –12 = 69 |
Q46. The mean of the median, mode and range of the observation 6, 6, 9, 14, 8, 9, 9, 8 is
(a) 8.5
(b) 8.8
(c) 10.3
(d) 10.5
| Answer: (a) 8.5 Explain: Arrange the given value in ascending order 6, 6, 8, 8, 9 , 9, 9, 14 Hence given sequence have even number then middle value are 8 and 9 ∴ Median = 8+92=8.5 Mode = value that appears maximum number of times = 9 Range = maximum value – minimum value = 14 – 6 = 8 Required mean = 8.5+9+83=8.5 |
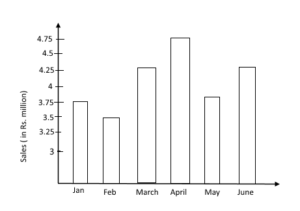
Q 47. According to the given graph, between which two consecutive months was the change in the auto sales the greatest?
(a) January – February
(b) February – March
(c) April – May
(d) May – June
| Answer: (c) April – May Explain: Sales in January = 3.75 million Sales in February = 3.5 million Sales in March = 4.25 million Sales in April = 4.75 million Sales in May = 3.75 million Sales in June = 4.25 million Sales Change January – February = 3.75 – 3.5 = 0.25 million February – March = 4.25 – 3.5 = 0.75 million April – May = 4.75 – 3.75 = 1 million May – June = 4.25 – 3.75 = 0.50 million From the given data, it can be observed that change in sales is highest from April to May. |
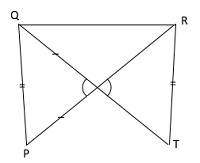
Q48. In the figure, in triangle PQR and TQR, PQ = TR and PR = TQ. Which of the following statements is true?
(a) ∆PQR ≅ ∆ TRQ
(b) ∆PQR ≅ ∆ TQR
(c) ∆PQR ≅ ∆ RQT
(d) ∆PQR ≅ ∆ QTR
| Answer: (a) ∆PQR ≅ ∆ TRQ Explain: PQ = TR, PR = TQ and QR is the common side of two triangles. As all three sides of both triangles are equal, the given triangles are congruent The angle corresponding to ∠P is ∠Q and that is corresponding to ∠R. Therefore, ∆PQR and ∆TRQ are congruent. |
Q49. The least number which is a perfect square and is also divisible by 10, 12, 15 and 18 is
(a) 3600
(b) 2500
(c) 1600
(d) 900
| Answer: (d) 900 Explain: Any number is divisible by a given set of numbers if that number is divisible by the LCM of the numbers. LCM of 10, 12, 15 and 18 = 180; 900 is the least number that is divisible by 180. It is also a perfect square. Hence, 900 is the required number. |
Q50. How many lines of symmetry does a parallelogram have?
(a) 3
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) None
| Answer: (d) None Explain: A parallelogram does not have any line of symmetry. |
Q51. Ankur got zero marks n a word problem on linear equations in an assessment. The teacher knows that he can solve linear equations correctly. The teacher ought to remark in his report that
(a) Ankur is not studying and practicing at home.
(b) Ankur has not understood the concept of linear equations completely.
(c) Ankur has a problem in comprehending the language of the question, though he can solve the equations.
(d) Ankur lacks concentration and hence has examination phobia.
| Answer: (c) Ankur has a problem in comprehending the language of the question, though he can solve the equations. Explain: Ankur has a problem in comprehending the language of the question, though he can solve equations. Providing assistance to such students (through pictures or suitable manipulators) in understanding problems and making them solve a number of similar problems will be helpful. Slowly, they will learn to think abstract terms like other students in the class. |
Q52. A suitable approach to introduce ‘Coordinate Geometry’ in Class IX is through the use of
(a) lecture method
(b) role play
(c) demonstration using technology integration
(d) solving problems
| Answer: (c) demonstration using technology integration Explain: Technology integration using technology to enhance the understanding of students in a particular subject. For subjects like coordinate geometry, Geo-algebra very effective. The teacher can demonstrate it in the class, or the students can experience the joy learning themselves by using this software on à computer.
|
Q53. Summative assessment of the unit ‘Mensuration’ can be done through
(a) project work
(b) maths lab activity
(c) paper-pencil test
(d) ICT activity
| Answer: (c) paper-pencil test Explain: Summative assessment is the ‘assessment of learning. i.e., to assess how much the student has learnt. This is done by a paper-pencil test that consists of a fixed number of questions to be completed in a given time period. The students are graded on the basis of the scores they obtain in the test. |
Q54. While solving a problem based on Pythagoras theorem, a teacher draws the following triangle ABC:
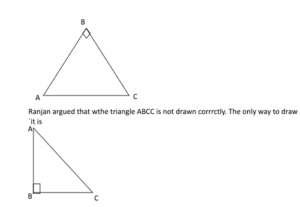
Rajan has the misconception as
(a) he is weak in geometrical concepts
(b) his teacher must have always drawn the triangle this particular way
(c) he has dysgraphia
(d) he lacks in analytical ability
| Answer: (d) he lacks in analytical ability Explain: Most of the time, he saw the right-angled triangle as he had drawn, but he could not analyze that his teacher also drew a right-angled triangle: only the position of the angle had changed. |
Q55. In order to help the students with difficulties in remembering the geometrical terms and their meaning. a teacher must
(a) stress on rote memorization of all terms and definitions
(b) use lots of activities like preparing or solving crossword puzzles, Jig-saw puzzles, etc.
(c) test students on the definition of geometrical terms
(d) encourage group discussions
| Answer: (b) use lots of activities like preparing or solving crossword puzzles, Jig-saw puzzles, etc. Explain: Repeated use of terms through activities like crossword or jigsaw puzzles, quizzes, etc., helps students remember difficult terms and their meanings. |
Q56. While teaching ratio and proportion, Ms. Rama demonstrated some computer operations on the screen – copy and paste and ‘copy and enlarge or copy and reduce. This activity may be
(a) pre-content activity to introduce ratio
(b) post-Content activity
(c) formative assessment activity
(d) Fun activity to pass time
| Answer: (a) pre-content activity to introduce ratio Explain: The students will get an idea of ratio and proportion when they see their teacher demonstrating ‘copy and paste’ and ‘copy and enlarge’ or copy and reduce” and explaining how many times the image has been enlarged or reduced. She may draw the attention of the students towards the proportionate increase or decrease in the size of the image. |
Q57. A student observed the following examples:
(10)2 = (5+5)2 = (5)2 + 2(5)(5)+ (5)2 = 100
= (6 + 4)2 = (6)2 + 2(6)(d)+ (d)2 = 100
= (8 + 2)2 = (8)2 + 2(8)(b)+ (b)2 = 100
= (9 + 1)2 = (9)2 + 2(9)(a)+ (a)2 = 100
and concluded that
(a +b)2 = a2 + 2(a)(b) +b2
The above method of drawing conclusions is
(a) deductive
(b) inductive
(c) analytical
(d) activity
| Answer: (b) inductive Explain: It is an inductive method wherein a number of examples are given and students find the common feature in all of them and generalize the result. So, it is a method of constructing a formula with the help of a sufficient number of concrete examples. An inductive approach is based on psychological principles: particular to general, concrete to abstract, known to unknown, simple to complex, etc. |
[ Read: 2011 June CTET Paper-I Questions with Answer ]
Q58. Mr. Manish used lots of manipulative, math lab activities and ICT activities to clarify the concept of Symmetry’. Mr. Manish wants to
(a) cater to students of all learning styles
(b) be popular amongst his students
(c) pass time so that he can avoid teaching of next topic, as it is not of his interest
(d) cater to kinesthetic learners only
| Answer: (a) cater to students of all learning styles Explain: Manish knows that there are students with different learning styles in his class. He uses a combination of different methods to teach the concept of symmetry so that all the students are benefitted from one or the other. |
Q59. Problem solving method is the
(a) gradual and systematic guiding through the hierarchy of mathematical notions, Ideas and techniques
(b) teaching of mathematical results, definitions and concepts by repetition and memorization
(c) teaching the development of mathematics within a historical, social and cultural context
(d) cultivation of mathematical ingenuity, creativity and heuristic thinking by making students open-minded
| Answer: (a) gradual and systematic guiding through the hierarchy of mathematical notions, Ideas and techniques Explain: The problem-solving method is a gradual and systematic guiding through the hierarchy of mathematical notions, ideas and techniques. This method makes students retrieve their prior information and apply it to the problems based on new or varying situations. |
Q60. Salman solves – 3 – 4 = +7.The error is committed as
(a) Salman is careless
(b) Salman is not clear about the concept of addition of integers
(c) Salman needs to practice solving problems of Similar type
(d) Salman has not understood the concept of multiplication of integers
| Answer: (b) Salman is not clear about the concept of addition of integers Explain: He has confused it with multiplication where (–) (–) become (+). |
Q61. The following observations were made by students A, B, C and D when they rubbed solid baking soda on dry litmus paper:
| Student | Effect on Dry Red Litmus Paper | Effect on Dry Blue Litmus Paper |
| A | Color changed to blue | No change |
| B | No change | Color changed to red |
| C | Color changed to blue | Color changed to red |
| D | No change | No change |
The correct observation was made by the student
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
| Answer: (a) A Explain: Litmus paper is used for testing the acidic or basic nature of a substance. There are two color litmus papers, i.e., red and blue. If red litmus turns blue on dipping in a solution, it shows the given solution is basic. f blue litmus turns red on dipping in a solution, it shows the given solution is acidic, Baking soda is basic in nature so it would convert the red litmus to blue. |
Q62. A laboratory thermometer shows five small divisions between the markings of 55°C and 56°C. This means that the thermometer can read correctly up to
(a) 55.1 °C
(b) 55.5°C
(c) 55.2°C
(d) 55.25°C
| Answer: (c) 55.2°C Explain: There are nine sub-divisions (0.1-0.9) between two markings. If there are five mall divisions between two markings, then it shows that each sub-division covers a reading of 0.2. So, if there are five small divisions between 55°C and 56°C then each small division can read up to 55.2°C and so on. |
Q63. Which of the following group of words can be correctly identified with Rhizobium?
(a) Root nodules, pitcher plant, nitrogen deficient soil
(b) Nitrogen fixation, root nodules, leguminous plants
(c) Roots of legumes, parasite, soluble nitrogen compounds
(d) Leguminous plants, symbiotic, stem nodes
| Answer: (b) Nitrogen fixation, root nodules, leguminous plants Explain: Rhizobium is a bacterium found in the root nodules of the leguminous plants. It is capable of fixing the nitrogen present in the soil into the forms that can be easily absorbed by the plants. |
Q64. When carbon dioxide is passed through clear lime water solution, it turns milky. The milky appearance of lime water is due to the
(a) presence of impurities in lime water
(b) presence of insoluble calcium carbonate
(c) presence of soluble calcium carbonate
(d) curdling of milk due to lime in lime water
| Answer: (b) presence of insoluble calcium carbonate Explain: Insoluble calcium carbonate is formed when carbon dioxide is passed through lime water. This gives a milky appearance to the lime water. the reaction that occurs is as follows: CO2 (aq) +Ca(OH)2 (ag) → CaCO3 (s) + H2O |
Q65. When electric current is passed through a metallic conductor, amount of heat produced in the conductor depends on its
(a) material and length only
(b) length and thickness only
(c) material and thickness only
(d) material, length and thickness
| Answer: (d) material, length and thickness Explain: The amount of heat produced by a metallic conductor on passing the electric current depends upon three following: Material: as less heat is produced by good conductors Thickness: as production of heat decreases with increase in the thickness Length: as production of heat increase with increase in the length |
Q66. PET bottles and jars are commonly used for storing edible items. PET is a very familiar form of
(a) Polyester
(b) Acrylic
(c) Rayon
(d) Polyamide
| Answer: (a) Polyester Explain: PET (polyethylene terephthalate) is commonly used polyester for making clothing fibers, food and liquid containers. It is commonly referred to as polyester (common name of PET). Acrylic and rayon are artificial fibers whereas polyamide is a heteropolymer that naturally occurs in wool and silk. |
Q67. The minerals that are required in the right amount for proper functioning of muscles are
(a) iron and calcium
(b) sodium and potassium
(c) iodine and fluorine
(d) iron and iodine
| Answer: (b) sodium and potassium Explain: The minerals required for proper functioning of muscles are sodium, magnesium and potassium. Iodine plays a role in functioning of thyroid gland. Iron helps in formation of blood cells while fluorine helps in preventing the dental caries. Calcium is important for making the teeth and bones strong. Deficiency of sodium and potassium causes muscle weakness and muscle Cramps, respectively. |
Q68. Antibiotics are effective against
(a) dengue fever
(b) cholera
(c) influenza
(d) hepatitis A
| Answer: (b) cholera Explain: Antibiotics are given for fighting bacterial diseases such as cholera and typhoid. Dengue, hepatitis A and influenza are viral diseases. |
Q69. When CNG or LPG undergoes complete combustion the products formed are
(a) CO2 only
(b) CO2, CO and H2O
(c) CO2 and H2O
(d) CO2, SO2 and H2O
| Answer: (c) CO2 and H2O Explain: Combustion is the process in which substances are burnt in air or Oxygen with the evolution of light and heat. Complete combustion Occurs when a fuel is burnt with enough oxygen to Support the process of burning and converting all of the carbon into carbon dioxide. Water and energy are also released during this process. |
Q70. The smallest of living organisms with cell wall are
(a) cyanobacteria
(b) bacteria
(c) yeast
(d) algae
| Answer: (b) bacteria Explain: Bacteria includes the smallest species o organisms on Earth with a wide variation in their sizes. They possess a rigid cell wall to protect themselves. Cyan bacteria are not the smallest bacteria. |
Q71. The process of converting sugars into alcohols is known as
(a) homogenization
(b) fermentation
(c) pasteurization
(d) sterilization
| Answer: (b) fermentation Explain: Fermentation is a process in which sugar (glucose) is converted into alcohol (ethanol) with a release of carbon dioxide. It is a form of anaerobic respiration that occurs naturally in yeast. The reaction that occurs is as follows. C6 H12 O6 → 2 C2 H5OH +CO2 |
Q72. The SI unit of calorific value is
(a) KJ /K
(b) Calorie
(c) J/kg
(d) Kilocalorie /kg
| Answer: (b) Calorie Explain: The calorific value of a fuel is the amount of heat generated when 1 kg of the fuel burns completely. It is commonly expressed in terms of J/kg, however, its SI unit is joule per Kilogram 0/kg). |
Q73. Given below are a few chemical processes:
- Rusting of iron
- Burning of a candle
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
Which two of these represent slow combustion?
(a) 2 and 3
(b) 2 and 4
(c) 4 and 1
(d) 1 and 3
| Answer: (a) 2 and 3 Explain: Slow combustion refers to the process of combustion occurring at low temperatures that produces less amount of heat. Respiration and burning of a candle are examples of slow combustion as they occur at low temperatures. Rusting of iron is an oxidation reaction but it is not combustion as energy is not released during this process. Similarly, in photosynthesis, there is no release of energy thus, it is also not a combustion reaction. |
Q74. Which one of the following man-made fibers is also called artificial silk?
(a) Nylon
(b) Rayon
(c) Acrylic
(d) Polyester
| Answer: (b) Rayon Explain: Rayon is a manmade fiber which is also referred to as artificial silk due to its appearance that resembles silk. It is made from the cellulose obtained from wood pulp. |
Q75. If the frequency of vibrations of a body is decrease and its amplitude is increased, then
(a) both pitch and loudness of sound produced will decrease
(b) both pitch and loudness of sound produced will increase
(c) pitch increases but loudness decreases
(d) pitch decreases but loudness increases
| Answer: (d) pitch decreases but loudness increases Explain: The frequency of sound determines the pitch of the sound, whereas the amplitude of sound determines the loudness of the sound. If the frequency of sound is more, the pitch will be higher and vice versa. Similarly, a high amplitude sound is louder than the sound of low amplitude. |
Q76. The dietary fibers are
(a) also called roughage
(b) made up of cellulose and proteins
(c) made up of collagen fibers
(d) made up of proteins
| Answer: (a) also called roughage Explain: Roughage (dietary fibers) is the part of the plant food products that humans are unable to digest. The dietary fibers contain cellulose that cannot be digested by humans. |
Q77. Which of the following statements related to earthquakes is not correct
(a) The Richter Scale is not linear but logarithmic.
(b) The seismic waves originate from focus.
(c) The record o the seismic waves is called seismograph.
(d) The seismograph records the seismogram.
| Answer: (d) The seismograph records the seismogram. Explain: Seismograph is a device that records the seismic waves (waves of energy travelling in the layers of Earth) that originate from the focus (epicenter) of the earthquake. |
Q78. The gas forms carboxyl hemoglobin in the blood, that causing suffocation is
(a) carbon dioxide
(b) chlorofluorocarbon
(c) carbon monoxide
(d) nitrogen
| Answer: (c) carbon monoxide Explain: Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas that interferes with the binding of oxygen to hemoglobin, which is required for the transport of oxygen in the body. It has a higher affinity to bind with hemoglobin than oxygen and may cause suffocation if inhaled. |
Q79. The gases present in the atmosphere that cause the greenhouse effect are
(a) carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, methane
(b) nitrous oxide, oxygen, water vapor
(c) methane, water vapor, carbon dioxide
(d) carbon dioxide, oxygen, nitrogen
| Answer: (c) methane, water vapor, carbon dioxide Explain: Greenhouse gases are gases that cause the greenhouse effect. The main greenhouse gas in the atmosphere is carbon dioxide. Other greenhouse gases are methane, nitrous oxide, fluorinated Bases, and water vapors. |
Q80. In order to determine the acidic, basic or neutral character of solutions, a student tabulated the following results after experimentation. Which of the following observations has been tabulated correctly?
| Case | Test Solution | Color Change on Red Litmus Paper | Color Change on Blue Litmus Paper | Acidic/ Basic/ Neutral |
| A | NaCl | No change | Red | Acidic |
| B | Lime water | Blue | No change | Neutral |
| C | Vinegar | No change | No change | Neutral |
| D | Washing Soda | Blue | No change | Basic |
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
| Answer: (d) D Explain: Litmus paper is used for testing the acidic or basic nature of a substance. There are two color litmus papers, i.e. red and blue. If red litmus turns blue on dipping in a solution, it shows the given solution Is basic. If blue litmus turns red on dipping in a solution, it shows the given solution is acidic. Sodium chloride is neutral; so, there will be no change in color of the litmus paper. Lime water and washing soda are basic; thus, they will change the red litmus blue. Vinegar is acidic; so, it will change the blue litmus red. |
Q81. A Science teacher is interested to focus more on the acquisition of process skills by the learners. Which of the following combination of methods of teaching should be preferred by her to achieve the objectives?
(a) Assignment-cum-questioning method
(b) Lecture-cum-discussion method
(c) Project-cum-laboratory method
(d) Lecture-cum-demonstration method
| Answer: (c) Project-cum-laboratory method Explain: A combination of project cum laboratory method should be used by the teacher. In both of these methods, students have to use process skills like identifying a problem, defining the problem, making a hypothesis, testing hypothesis by different ways experimentation, selection of apparatus, setting apparatus, taking readings, measurements, recording data, data analysis, making conclusions, comparing results etc. These skills are not used in lecture, questioning, demonstration or assignments. |
Q82. Which of the following is most suited to the development of scientific skills in students?
(a) Conducting science quiz
(b) Organizing a field visit
(c) Conducting science Olympiads
(d) Performing laboratory work
| Answer: (d) Performing laboratory work |
Q83. Which one of the following is the major objective of teaching Science at upper primary stage?
(a) To promote rational thinking
6) To remember the names of scientists and scientific discoveries
(c) To learn important facts and formulae
(d) To develop proficiency in solving exercises given at the end of the chapter
| Answer: (a) To promote rational thinking Explain: Out of the four options given, top promote rational thinking is the major objective as t prepares the person to solve problems and take logical decisions without getting impulsive or illogical. |
Q84. Practical work in Science may be given due emphasis in order to
(a) improve the percentage of marks obtained by the students
(b) help the students develop the habit of maintaining written records
(c) keep a proper check on punctuality and regularity of students
(d) help the students verify the theoretical concepts
| Answer: (d) help the students verify the theoretical concepts |
Q85. Project method in the teaching of Science is suited most to
(a) promote understanding of basic concepts
(b) enhance the numerical abilities of students
(c) strengthen reasoning skill of studies
(d) promote the scientific method of working
| Answer: (d) promote the scientific method of working |
Q86. The constructivist approach in the teaching of Science refers
(a) Applying different mathematical formulae in solving problems
(b) Providing experiential learning to students
(c) Providing more and more reading material to students
(d) Providing additional academic help to weak students
| Answer: (b) providing experiential learning to students |
Q87. Which one of the following is the key feature of Formative Assessment in Science?
(a) It is conducted at the end of the year.
(b) It is diagnostic in nature.
(c) It is aimed at developing scientific temper in the students.
(d) It is called enhancing practical skills.
| Answer: (b) It is diagnostic in nature. |
Q88. Summative Assessment in Science should mainly focus on
(a) Testing of mainly practical skills.
(b) Testing important theoretical concepts.
(c) Assessing observation skills.
(d) Diagnosing the areas of learning difficulties of students.
| Answer: (b) testing important theoretical concepts. |
Q89. One of the main limitations of the Project method of teaching Science is that
(a) The students have to perform excessive mental and physical work.
(b) It is a psychological method.
(c) Knowledge is not acquired in a sequential manner.
(d) Integration of concepts in various subjects can be achieved.
| Answer: (c) knowledge is not acquired in a sequential manner. |
Q90. Assessment in Science should focus more on testing the ability of students to
(a) State the facts and principles of science correctly
(b) Apply the understanding of concepts to unfamiliar situations in everyday life
(c) Answer open-ended questions
(d) Be sufficiently equipped for higher learning
| Answer: (b) apply the understanding of concepts to unfamiliar situations in everyday life |
