CTET 2014 September Paper-1 Question with Answer | ||
| Child Development | Mathematics | EVS |
| Language – I (Eng) | Language – II (Hindi) | |
Mathematics
DIRECTIONS: Answer the following questions by selecting the most appropriate option.
Q31. The difference between the place value and the face value of 5 in 35362 is
(a) 50
(b) 495
(c) 4995
(d) 5005
| Answer: (c) 4995 Solution: place value of 5 in 35362 is 5000 Face value of 5 in 35362 is 5 ∴ Difference of the place value and the face = 5000 – 5 = 4995 |
Q32. 10 ones + 10 tens+ 10 thousands equals
(a) 11100
(b) 101010
(c) 10110
(d) 11011
| Answer: (c) 10110 Solution: 10 ones + 10 tens+ 10 thousands = 10 × 1 + 10 × 10 + 10 × 1000 = 10110 |
Q33. The sum of the positive factors of 210 is
(a) 576
(b) 575
(c) 573
(d) 366
| Answer: (a) 576 Solution: factors of 210 are 210, 105, 70, 42, 35, 30, 21, 15, 14, 10, 7, 6, 5, 3, 2, 1 ∴ Their sum = 210 + 105 + 70 + 42 + 35 + 30 + 21 + 15 + 14 + 10 + 7 + 6 + 5 + 3 + 2 + 1 = 576 |
Q34. Gorang worked 4½ hours on Monday, 190 minutes on Tuesday, from 5: 20 a.m. to 9: 10 a.m. on Wednesday, and 220 minutes on Friday. He is paid 42 per hour. How much did he earn from Monday to Friday?
(a) Rs. 560
(b) Rs. 580
(c) Rs. 540
(d) Rs. 637
| Answer: (d) Rs. 637 Solution: Gorang worked = 412+19060+35060+22060 = 92+19060+23060+22060 =270+190+230+22060 = 91060=916hr He earn = 916×42=637 |
Q35. The sum of the greatest 4-digit number and the smallest 3-digit number is
(a) 7000
(b) 9899
(c) 10099
(d) 10999
| Answer: (d) 10999 Solution: greatest 4-digit number = 9999 Smallest 3-digit number = 100 ∴ Required sum = 9999 + 100 = 10999 |
Q36. Twenty-six and twenty-six hundredths are written as
(a) 2626
(b) 26.26
(c) 262.6
(d) 2.626
| Answer: (b) 26.26 Solution: Twenty-six = 26 and twenty-six hundredths = 26100=0.26 Twenty-six and twenty-six hundredths = 26 + 0.26 = 26.26 |
Q37. The product of remainders of 19009 ÷ 11 and 9090 ÷ 11 is
(a) 4
(b) 5
(c) 8
(d) 12
| Answer: (a) 4 Solution: remainder when 19009 divided by 11 = 1 And remainder when 9090 divided by 11 = 4 ∴ Required product = 4 × 1 = 4 |
Q38. How many 1/6 are there in 3⅓?
(a) 12
(b) 15
(c) 18
(d) 20
| Answer: (d) 20 Solution: Required = 31316=103×6=20 |
Q39. What number should be subtracted from the product 1109 x 505 so as the get 505050?
(a) 49495
(b) 55005
(c) 54995
(d) 54995
| Answer: (d) 54995 Solution: product = 1109 x 505 =560045 ∴ Required number = 560045 – 505050 = 54995 |
Q40. Which of the following is not correct?
(a) 1 mm is one-tenth of 1 cm
(b) 1 kg 12 grams = 1.012 kg
(c) 10 meter 10 cm = 1010 cm
(d) 23/100 = 2.30
| Answer: (d) 23/100 = 2.30 Solution: 10 mm = 1 cm, ∴ 1 mm = 110 cm 1 kg 12 grams = 1 + 121000 = 1.012 kg 10 meter 10 cm = 1000 + 10 = 1010 cm 23/100 = 0.23 So, option (d) incorrect. |
Q41. A tank contains 240 liters (L) 128 milliliters (mL) of milk, which can be filled completely in 16 Jars of the same size. How much milk will be there in 22 such jars?
(a) 330 L, 176 ml
(b) 331 L, 176 ml
(c) 331 L, 760 ml.
(d) 332 L, 650 ml
| Answer: (a) 330 L, 176 ml Solution: Tank contain milk = 240 liters 128 milliliters = 240000 + 128 = 240128 ml Milk in 1 jar = 24012816=15008ml Milk in 22 jar = 22 × 15008 = 330176 ml = 330 L 176 ml |
Q42. Number of degrees in four and two-third right-angles is
(a) 310
(b) 420
(c) 330
(d) 400
| Answer: (b) 420 Solution: right-angle = 90° four and two-third right-angles = (4+23)×90= 420° |
Q43. A water tank is 11 m long, 10 m wide and 9 m high. It is filled with water to a level of 6m. What part of the tank is empty?
(a) 1/4
(b) 1/3
(c) 1/6
(d) 2/3
| Answer: (b) 1/3 Solution: Volume of tank = 11 × 10 × 9 = 990 m3 Volume of empty portion = 11 × 10 × (9 – 6) = 330 m3 part of the tank is empty = 330/990 = 1/3 |
Q44. The perimeters of a rectangle and a square are equal. The perimeter of the square is 96 cm and the breadth of the rectangle is 4 cm less than the side of the square. Then two times the area (in square cm) of the rectangle is
(a) 560
(b) 960
(c) 1120
(d) 1040
| Answer: (c) 1120 Solution: Let side of square = a cm ∴ 4a = 96 ⇒ a = 24 Breadth of the rectangle = 24 – 4 = 20 Let length of the rectangle = b ∴ 2(b + 20)=96 ⇒ b = 48 – 20 = 28 two times the area of the rectangle = 2 × 28 × 20 = 1120 cm2 |
Q45. The difference of (smallest common multiple of 4, 5, and 6) and (smallest common multiple of 5, 6, and 9) is
(a) 30
(b) 45
(c) 48
(d) 60
| Answer: (a) 30 Solution: smallest common multiple or LCM of 4, 5, and 6 = 60 smallest common multiple or LCM of 5, 6, and 9 = 90 ∴ Required difference = 90 – 60 = 30 |
Q46. As per NCF 2005, the teaching of numbers and operations on them, measurement of quantities, etc. at the primary level caters to the
(a) narrow aim of teaching mathematics
(b) higher aim of teaching mathematics
(c) aim to mathematics the child’s thought process.
(d) aim of teaching important mathematics
| Answer: (a) narrow aim of teaching mathematics |
Q47. In Class 3, a teacher asked the students to add 4562 and 728. A student responded to the questions as follows
4562
+728
…………
11842
The response reflects that the child lacks the
(a) Skill of addition
(b) Concept of place value
(c) Skill of addition by regrouping
(d) Concept of addition
| Answer: (b) Concept of place value |
Q48. Which of the following problems from the textbook of Class IV refers to the multidisciplinary problem’?
(a) Draw the flag of India and identify the number of lines property of addition of symmetry in the flag
(b) Draw the mirror image of a given figure
(c) How many lines of symmetry are there in a given
(d) To draw a line of symmetry in a given geometrical figure.
| Answer: (a) Draw the flag of India and identify the number of lines property of addition of symmetry in the flag |
Q49. The following grid is drawn on a square paper figure?
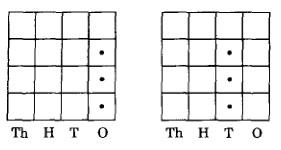
This representation reflects
(a) position of numbers on the abacus
(b) concept of place value
(c) equivalence of tens and ones
(d) mathematical game
| Answer: (b) concept of place value |
Q50. Children at the primary stage are able to classify the given shapes based on their appearance. According to Van Hiele levels of geometry, they are at
(a) Visualization stage
(b) Analytic stage
(c) Informal deduction stage
(d) Formal deduction stage
| Answer: (a) Visualization stage |
Q51. Manipulative models, static pictures, written symbols, spoken and written language, real-world situation or contexts are five ways to represent
(a) Mathematical thinking and ideas
(6) Geometrical proof
(C) Mathematics curriculum
(d) Mathematical vocabulary
| Answer: (a) Mathematical thinking and ideas |
Q52. After teaching the concept of division, a teacher-created Mathematical Wall’ in the classroom and asked the students to write any two division facts in the assigned columns within 48 hours
| MATH WALL | |||
| Ankit 25 ÷ 5 = 5 | Auku 0 ÷ 6 = 0 | Babita | Bobby |
| Pragya | Dhruv | Sohan | Harsh |
| Rahul | Smita | Sunil | Tushar |
This activity can help the teacher to
(a) make the classroom environment noise-free
(b) engage the students for the next two days in some mathematical work
(c) give an opportunity of expression to every child and to learn from each other
(d) keep the record of the number of facts learned by the students
| Answer: (c) give an opportunity of expression to every child and to learn from each other |
Q53. A possible indicator pertaining to visual memory barrier hampering with learner’s mathematical performance is
(a) difficulty in retaining mathematical facts and difficulty in telling time
(b) difficulty in using a number line
(c) difficulty to count on within a sequence
(d) difficulty in handling small manipulations
| Answer: (a) difficulty in retaining mathematical facts and difficulty in telling time |
Q54. A teacher in Class-III distributed the following cards and asked the children to match the same shapes.
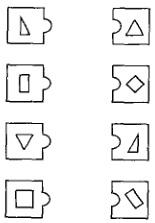
The objective of this game is to
(a) make the classroom environment engaging and joyful
(b) help children to recognize the same shapes in different orientations
(c) enhance eye-hand coordination
(d) develop the concept of similarly and congruency
| Answer: (b) help children to recognize the same shapes in different orientations |
Q55. Geo-Board is an effective tool to teach
(a) basic geometrical concepts like rays, lines, and angles
(b) geometrical shapes and their properties
(c) difference between 2D and 3D shapes
(d) concepts of symmetry
| Answer: (b) geometrical shapes and their properties |
Q56. Proficiency in Mathematical language in the classroom can be enhanced by presenting the problem in the following Sequence.
(a) Everyday language → Mathematized situation language → Language of Mathematical problem solving → Symbolic language
(b) Symbolic language → Language of Mathematical problem-solving → Mathematized situation language → Everyday language
(c) Everyday language → Language of Mathematical problem-solving → Mathematized situation language → Symbolic language
(d) Language of Mathematical problem-solving → Mathematized situation language → Symbolic language → Everyday language
| Answer: (a) Everyday language → Mathematized situation language → Language of Mathematical problem solving → Symbolic language |
Q57. Procedural fluency in Mathematics implies knowledge of rules, formulae, or algorithms and implementing them with accuracy and flexibility, and efficiency. Flexibility in Mathematics refers to
(a) ability to solve different types of problems from the same topic
(b) ability to solve problems from arithmetic and geometry with the same efficiency
(c) ability to solve a particular Kind of problem using more than one approach
(d) ability to solve problems with accuracy, writing all steps
| Answer: (c) ability to solve a particular Kind of problem using more than one approach |
Q58. A child mentally calculated (27+38) as 65. When he was asked to explain his method of addition, he responded that 38 is near to 40 so (27+40) is 67, then I removed 2 to get 65. This strategy of addition is
(a) Direct modeling
(b) Regrouping
(c) Compensating
(d) Incrementing
| Answer: (c) Compensating |
Q59. Mental Math activities are important because they provide a chance to
(a) Developmental computation procedures as the students try to identify the relationship between numbers for fast calculations
(b) master procedures learned in class using paper-pencil
(c) master algorithms learned and practice more number problems in less time
(d) develop their speed with accuracy for calculations and help to improve performance in examinations
| Answer: (a) Developmental computation procedures as the students try to identify the relationship between numbers for fast calculations |
Q60. A child of the primary class is not able to differentiate between numbers, operation symbols, coins, and clock hands. This indicates that the child has a problem regarding
(a) Auditory memory
(b) Working memory
(c) Visual processing
(d) Language processing
| Answer: (c) Visual processing |
